
Financial Malware
Financial malware is commonly used by fraudsters to take over devices and perform fraudulent activities.
For banks, devices infected with financial malware accessing their banking applications pose a challenging problem. Detecting financial malware on digital channels using traditional detection methods has limitations, as fraudsters employ effective measures to evade detection. ThreatMark focuses on malware behavior rather than its signature, making it a future-proof solution to reliably detect financial malware.
TALK TO A FRAUD FIGHTER
The scale of problem.
-
64%of banks reported a leak of confidential information caused by malware, in Q1-Q3 2023.
-
30%year-over-year growth of financial malware attacks.
-
1B+dollar annual global losses due to financial malware, estimates suggest.
Detect even the most sophisticated financial malware on digital channels.
The distribution of financial malware is primarily facilitated through deceitful tactics such as fraudulent e-mails and SMS or by using legitimate channels from trustworthy repositories, bypassing traditional security measures. After installing financial malware on the device, fraudsters can take complete control, allowing them to intercept communication, record screens and keystrokes, tamper with financial transactions, and create new ones.
Although traditional anti-virus could effectively detect financial malware, it has its limitations as cybercriminals constantly modify their software using various evasion techniques. Altering the characteristics to baffle signature-based anti-viruses, adaptively changing their behavior to confuse those behavior-based ones, and working strictly within the device memory to not leave a trace on the filesystem are a few examples.
ThreatMark’s behavioral intelligence platform offers an advantage over traditional anti-virus scanning methods. Instead of relying on signatures and traces on the filesystem, ThreatMark observes interactions with the banking application. By focusing on the subtle ways users interact with their devices (e.g., the mobile application initiates payment while the hardware sensors report that the mobile phone is perfectly still), ThreatMark can detect the presence of various types of malware that alter these interactions on all digital channels, in addition to traditional malware detection.

Detecting financial malware.
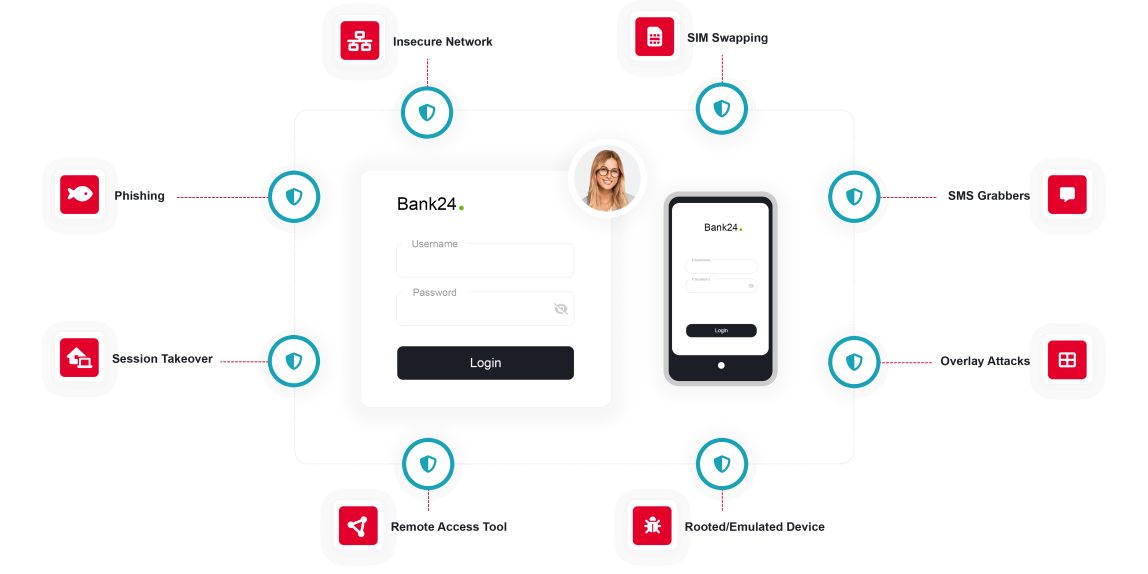
Mitigating financial malware with ThreatMark.
-
SIM Swap
SIM Swap is a growing global fraud in which an unauthorized person gains access to a SIM card and redirects all communication to their device, misusing the weakness of two-factor authentication.
Learn more
-
Session Hijacking
Session hijacking is a common fraudulent technique that gives fraudsters complete control over a victim's account. The fraudsters intercept and take control of a user's session token while logged in, leaving the victim unaware until their money is gone.
Learn More
-
Remote Access Attacks
Legacy fraud prevention measures have limited effectiveness in detecting remote access attacks. When a session is controlled remotely by fraudsters, the bank's systems may identify the device as trusted based on its fingerprint, which may not show any signs of malware and appear to have the correct IP and geo-location.
Learn More
Want to learn more about ThreatMark?
Complete our form to discover more about ThreatMark’s comprehensive approach to fraud disruption.